How to Check Blood Pressure with a Blood Pressure Cuff
Checking Blood Pressure with a Blood Pressure Cuff
About 45% of the adults living in the United States have high blood pressure. This health condition can cause strokes or heart disease and is life threatening if it is not kept under control. There are no signs or symptoms that are associated with it. That’s why it’s important to consistently check your blood pressure if you’re susceptible to this condition. For instance, you should consistently check your blood pressure if you’re elderly, overweight, or suffer from a certain chronic disease.
You do not need to go to the hospital every time you need to check your blood pressure. You can check it while in the comfort of your home using a blood pressure cuff from a good biomedical equipment seller, such as Coast Biomedical Equipment. Below are more details on how to use a sphygmomanometer to check your blood pressure.
How to Check Your Blood Pressure Using a Sphygmomanometer
The American Heart Association recommends that you remain seated while you are taking your blood pressure with the arm at the level of the heart. This means you could set your arm on a table, armrest, or something near that height.
The Procedure for Measuring Your Blood Pressure
To measure your blood pressure, do the following:
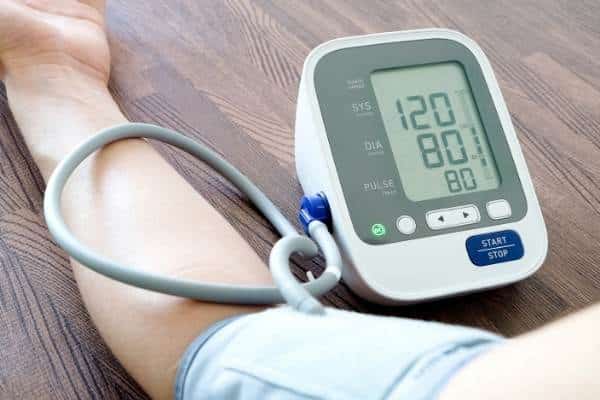
- Wrap the blood pressure cuff around your arm. Don’t wrap the cuff too tight. The lower edge of this cuff should be at least an inch above your elbow.
- After positioning the cuff in place, it should be inflated to about 30mmHg above your normal blood pressure. Ask your doctor for guidance. If you’re using a manual model, inflate the cuff using the hand pump. If you’re using a digital model, push the inflation button to inflate the cuff.
- Carefully and slowly release air from the cuff.
- Check the blood pressure reading on the sphygmomanometer after this equipment produces a knocking sound. This reading will be the systolic pressure.
- After the knocking sound disappears, record the reading on the sphygmomanometer. This reading will be diastolic pressure.
If you are using a stethoscope and a simple blood pressure cuff:
- Repeat the first two steps from above.
- Position your stethoscope in place near the elbow crease.
- Slowly release air from the cuff.
- When you hear a whooshing sound, remember the reading on the dial. This is the systolic blood pressure. The blood will continue pulsing, and once it stops, record the reading on the dial. This is the diastolic blood pressure.
It can be beneficial to take your blood pressure if you’re trying new medications, changing habits at home, or monitoring your overall heart health. Ask your doctor for further guidance about how to check your blood pressure at home.



