3 Tips for the Bariatric Patient’s Airway Management
Bariatric is a medical term used to describe treatment methods concerned with obesity. It is an extensive field of medicine that is focused on the causes and prevention of obesity as well as the promotion of weight loss in obese individuals. Although bariatrics is more often associated with a particular form of surgery also known as weight loss surgery, it also includes techniques such as diet, exercise, and therapy.
Bariatric patients are entitled to the same level of professional care as other patients. Due to their unique challenges, health care providers are expected to provide care to bariatric patients without harming their health and wellbeing. To ensure that they pose no risks to their health in the performance of their duties, EMS personnel are obligated to utilize specialized techniques and emergency medical equipment in the treatment or transportation of bariatric patients. To this end, here are some helpful tips to follow when faced with respiratory emergencies involving bariatric patients.
1. Approach The Problem With a Positive Mindset
Understandably, you’d have some doubts as to your ability to handle airway management in a patient weighing over 400 pounds. Forget about taking bigger breaths to make up for your patient’s size and instead consider that size is irrelevant when it comes to tidal volumes. The calculated tidal volume will help you perform your role effectively, so let go of the doubts and approach the situation from an objective and positive standpoint.
2. Place Your Patient In The Proper Position
The sniffing position remains constant in spite of patient weight. This implies that the bariatric patient should have his or her face parallel with the ceiling with the external auditory canal horizontally aligned with the top of the shoulder or sternum. If your patient is not positioned appropriately, your attempts at airway management will prove futile as airflow would be restricted. For a bariatric patient, you have to use whatever materials on hand to pad his or her shoulders; this will help you to keep the airway open and broaden the normoxic window so you can secure the airway device.
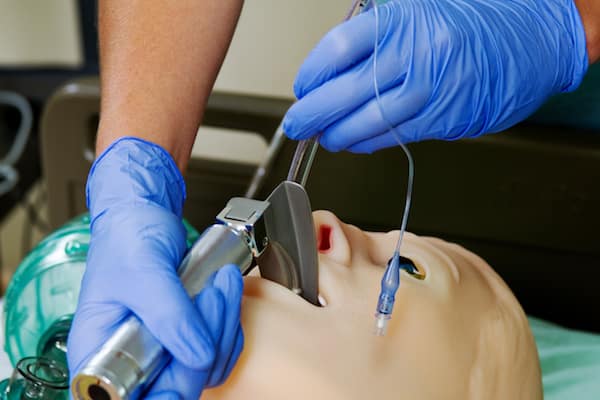
3. Have The Appropriate Equipment
For successful airway management, you need to possess the proper emergency medical equipment. These include a video laryngoscope, a suction unit, a bougie, etc.
In airway management, pre-oxygenation is vital. It buys you time to evaluate the situation and formulate a plan of action. With the tips provided above, you can effectively manage the airway of your bariatric patient. For more helpful tips and resources, visit the Coast Biomedical blog.




